Turbomachinery Research
Overview

Image Credit: Rolls-Royce. Source
Grand challenges
- More rigorously quantify the performance (and its breakdown) of existing compressors, pumps and turbines.
- Predict the performance of new turbomachinery systems with applcations in heavy and renewable industries.
Project Distorted
There is no shortage of metrics to quantify the spatial and radial distortion patterns commonly found in turbomachinery. Distorted is an open-source python framework for calculating all the well established distortion metrics for a given dataset. It has been verified and validated with SAE AIR1419, AIR5686 and ARP1420. Click on the logo below for source code and tutorials.

Project Aerobayes
Aerobayes has been part of a multi-year collaboration with Rolls-Royce. It is focused on developing probabilistic methods for more precisely inferring temperature and pressure spatial fields in engines using (i) data from installed temperature and pressure probes; (ii) data from other similar engines and rigs, and (iii) reduced order models (e.g., throughflow and CFD). This can enable better diagnosis of current engines (including anomaly detection) and more precise estimates in bids for future products. The core model is a spatial Gaussian process model with bespoke physics-based kernels.

Relevant publications are found below.
Machine Intelligent Pitot Probes
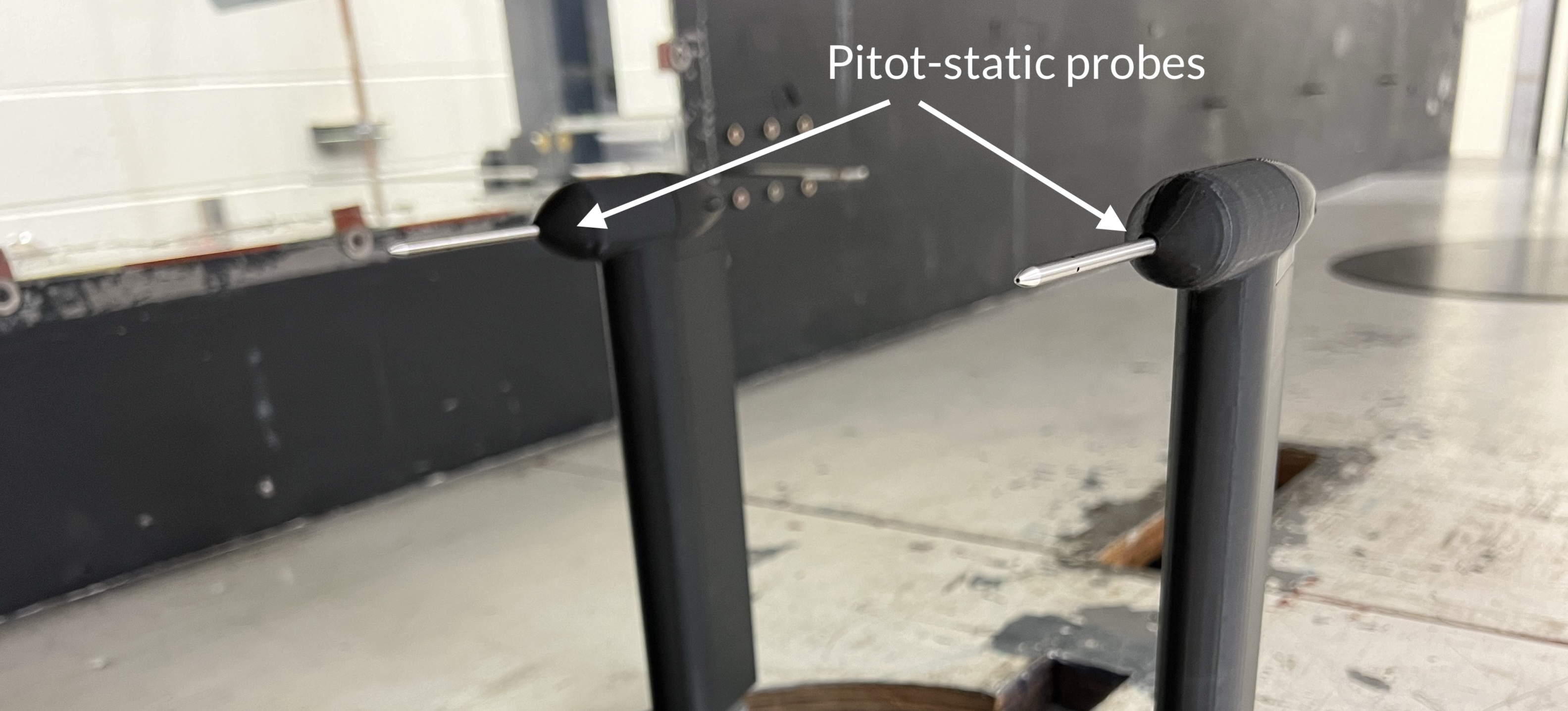
This project seeks to explore the utility of probabilistic time series models to calibrate pitot static probe measurements, especially in situations where different types of pressure transducers are used.
Large Aerofoil Models
This is an ongoing project with Juergen Rauleder & Howon Lee in the Vertical Lift Center for Excellence at Georgia Tech. We are building the largest experimental aerofoil repository and using that to build a model that can generate assessments of \(C_p\), \(C_l\), \(C_m\), and profile \(C_d\).



